Friends, today in this article we will learn about the structure and working of dynamometer type measuring instruments. I am going to give information about all these in a very good way. So let’s start.
Dynamometer type measuring instruments –
AC calibration cannot be done completely correctly in moving iron and other types of instruments, so transfer type instruments are required in them. Transfer instruments are instruments that can be calibrated with DC source and they can also be calibrated with AC source without any change. Therefore, the transfer type instrument should have the same accuracy with AC and DC source which is in the dynamometer instrument.
Dynamometer type instruments are used like AC voltmeter and ammeter which are also used for the lower part of power frequency and audio frequency.
Working principle of dynamometer type instrument –
In a dynamometer type instrument, torque is generated in one direction in one half cycle and torque of equal magnitude is generated in the opposite direction in the other half cycle. If the frequency of AC is very low then the pointer rotates and comes back to its initial state i.e. zero point. But for a normal meter, the value of inertia at the power frequency is very high, hence the pointer does not move very far and remains around zero.
If we change the direction of flux, then the direction of current in the coil changes every time and a unidirectional torque is generated for each positive and negative half cycle.
Hence, in a dynamometer type instrument, if the field coil (fixed) is connected in series with the movable coil, then along with the current, the field can also be reversed.
Structure of a dynamometer type instrument –
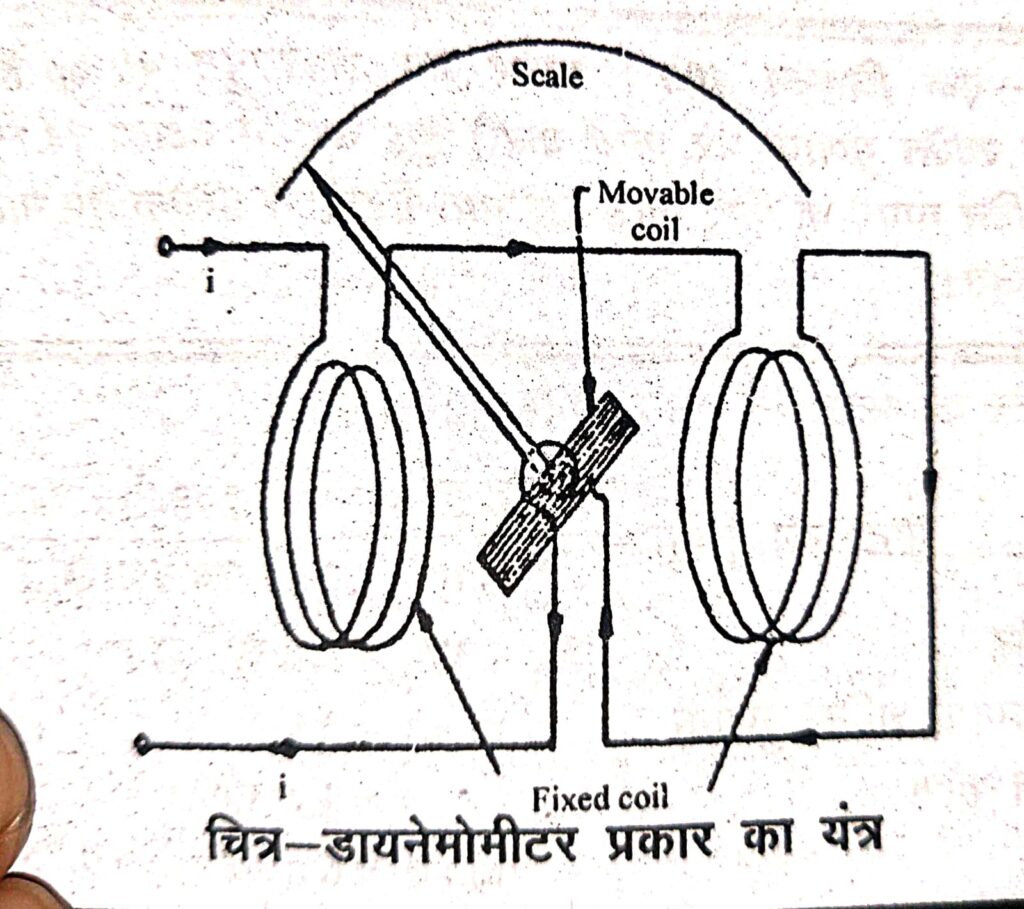
Fixed Coils – Field is generated by fixed coil. The coil is divided into two parts so that a uniform field is produced at the centre. (In the figure) a millimeter or voltmeter can be made by adding a series resistance. The fixed coil is wound with a thin wire.
Moving Coil – A single element instrument has only one moving coil. The moving coil is wound either like a self sustaining coil or on a non-metallic former. Generally metallic former is not used because it produces eddy current. It is important to note that both the moving and fixed coils are air cored.
Control – The controlling torque is provided by two controlling springs.
Moving System – The moving coil is mounted on an aluminium spindle. The moving system has a counter weight and a turns type pointer. Suspension is used in the moving system for high sensitivity.
Damping – An aluminium pair is attached to the spindle at the bottom of the instrument to provide air friction damping in these instruments. Eddy current damping is not used in these. The reason for this is the weak operating field in these instruments.
Shielding – The field generated by the fixed coil in these instruments is weak as compared to other instruments, which is about 0.005 to 0.006 Wb/m². In DC instruments, the earth’s magnetic field also affects the reading, so it is necessary that the dynamometer type instrument is shielded from the magnetic field. Therefore, this type of instrument is kept in a box made of high permeability alloy.
Cases and Scale – These instruments are kept in wooden boxes and a layer of glass is coated on the conducting material so that electrostatic effect is not generated and the structure is supported by an adjustable levelling screw. A sprit level is also used for correct leveling. High precision instrument has 100, 120, 150 divisions on a scale of 300 mm.
What did you learn today:-
Now you must have known the structure and working of dynamometer type measuring instruments. You must have got the answer to all these questions well.
I hope you liked the information given by me. If you have any question/suggestion in your mind, then you can tell me by commenting below. I will definitely answer your comment. If you liked this post, then you can also share it with your friends and relatives.
